I. Overview
The sedimentation method particle size test technology refers to the instrument and method for measuring the particle size distribution by the sedimentation speed of particles in the liquid. Here we mainly introduce the principles and methods of gravity sedimentation and centrifugal sedimentation particle size analyzers. In addition, pipettes and sedimentation balances are also devices of this type. Because they are used less now, they are not described here. Sedimentary particle size analysis generally involves mixing a sample with a liquid to make a suspension with a certain concentration. The particles in the liquid begin to settle under the action of gravity or centrifugal force. The settling speed of the particles is related to the size of the particles. The settling speed of the large particles is fast, and the settling speed of the small particles is slow. And particle size distribution. However, in the actual measurement process, it is difficult to directly measure the sedimentation speed of the particles. Therefore, the rate of change of the suspension concentration at a certain depth below the liquid level is usually used to indirectly determine the sedimentation speed of the particles, and then to measure the particle size distribution of the sample. When the largest particle does not drop from the liquid surface to the measurement area, the concentration there is in a constant state; when the largest particle falls to the measurement area, the concentration begins to decrease. As the sedimentation process progresses, the concentration will further decrease. Until all particles expected to be measured have settled below the measurement area, the measurement process ends. As shown in Figure 1:
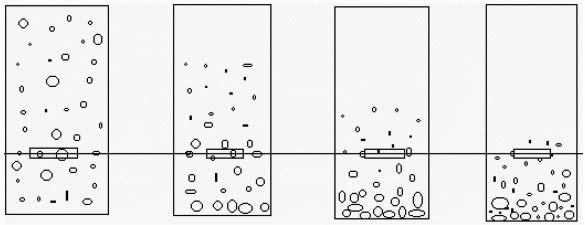 Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the sedimentation state of particles in the liquid
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the sedimentation state of particles in the liquid So, what is the relationship between the settling velocity of particles and the particle length? Stokes' law tells us that under certain conditions, the settling velocity of particles in a liquid is proportional to the square of the particle size and inversely proportional to the viscosity of the liquid. In this way, for coarser samples, we can choose a liquid with a larger viscosity as the medium to control the particle settling velocity in the center of the gravity field; for smaller particles, the settling velocity under the action of gravity is very slow, plus Brownian motion, The effect of changes in temperature and other conditions will increase the measurement error. In order to overcome these unfavorable factors, centrifugal means are commonly used to accelerate the sedimentation speed of fine particles. Therefore, in the current sedimentation particle size analyzer, the combination of gravity sedimentation and centrifugal sedimentation is generally adopted, so that gravity sedimentation can be used to measure coarse samples, and centrifugal sedimentation can be used to measure fine samples. In addition, there is a tracing settlement instrument that changes the depth of the measurement area, which is divided into dynamic and static types, which belongs to the gravity settlement model.
The new sedimentation particle size analyzer is an instrument that combines traditional theory with modern technology. It uses computer technology, microelectronic technology and even Internet technology, and has made great progress in instrument intelligence and automation. There are many types of it, such as BT-1500, SA-CP4, SG5100 and so on. The settling instrument has the following characteristics:
The operation and maintenance are simple and the price is low.
The continuous running time is long, and some can reach more than 12 hours.
Low running cost, less samples, less media consumption, less wearing parts.
The test range is wide, generally up to 0.1 ~ 200μ, with good repeatability and accuracy (true).
The test time is short, and the single measurement time is generally around 10 minutes.
The requirements on the environment are not high, and it can be operated at normal room temperature.
Since the actual particle shape is mostly non-spherical, it is impossible to express its size with a numerical value. Therefore, like other types of particle size instruments, the particle size measured by the sedimentation particle size analyzer is also an equivalent particle size, called the Stokes diameter. Stokes diameter refers to the diameter of homogeneous spherical particles with the same settling velocity as the measured particles under certain conditions. When the measured particles are spherical, the Stokes diameter is consistent with the actual diameter of the particles. In short, the sedimentation particle size analyzer is a kind of instrument with a wide range of applications. A good understanding of its principles, conditions of use, instrument characteristics and other aspects can better use it and play its due role. .
In short, the sedimentation particle size analyzer is a kind of instrument with a wide range of applications. A good understanding of its principles, conditions of use, instrument characteristics and other aspects can better use it and play its due role. .
Second, the principle
1. Stokes' Law: We know that the sedimentation particle size analyzer measures the particle size distribution through the sedimentation speed of particles in the liquid. When the particles settle in the liquid, there are three forces acting on the particles: downward gravity W, upward buoyancy V, upward resistance FD. According to Newton's laws of motion, its equation of motion is:
When the gravity, buoyancy, and viscous resistance reach equilibrium, the sedimentation speed of the particles is constant and is in a state of uniform velocity sedimentation. At this time,
Where D is the particle size, Ïs is the sample density, and Ïf is the medium density. In fluid mechanics, for the convenience of research and expression, a characteristic dimensionless number called Reynolds number is used, which is defined as follows: Reynolds number Re represents the ratio of inertial force to viscous force during fluid flow. When Re is small, the inertial force is negligible compared to the viscous force
The resistance of the particles at this time is completely caused by the viscous resistance of the liquid, which can be expressed by the following formula:
Where u is the sedimentation velocity of the particles and the viscosity coefficient of the η medium. This is the Stokes resistance formula. For research convenience, we also quote
The concept of drag coefficient is defined as:
Here A is the momentum energy per unit volume of fluid, and B is the projected area of ​​the particles in the direction of motion. From formula ⑷ and formula ⑸:
That is, when the Reynolds number Re is small, the drag coefficient is large. The figure below shows the relationship between Reynolds Re and resistance and CD when the spherical particles settle in the liquid. The figure is divided into three areas according to the Reynolds number: when Re <0.2, it is a laminar flow area, and when 0.22000 is a turbulent flow area.
Reynolds number (Re)
The applicable range of Stokes law is laminar flow area.
From equation (4), we can see that the resistance of the particles during sedimentation increases with the increase of speed. When the speed increases to a certain degree, gravity and resistance reach a balance, then substitute equation (4) into equation (2) to obtain:
This is Stokes's law.
Stokes' law expresses the relationship between sedimentation velocity and particle size under laminar flow conditions and is the theoretical basis for particle size measurement by the sedimentation method.
2. The critical diameter of gravity settlement
The above discussion shows that when Re> 0.2, the Stokes formula does not hold, so the diameter Ds calculated when Re = 0.2 is the critical diameter of gravity settlement. After combining equations (3) and (7), we get:
During the measurement, the measurement can be carried out only when the measured maximum particle size is less than the critical value, otherwise it will cause a large error. Table 1 shows the critical diameters (in microns) of some samples when they settle in several media at 20 ° C:
Table 1 Critical diameter of gravity settlement
When the maximum particle size of the measured sample is greater than the critical diameter, it is necessary to try to change the test conditions. From equation (8) and Table 1, it can be seen that increasing the viscosity of the medium can increase the critical diameter, so it is usually the reason to use glycerin aqueous solution as the coarse sedimentation medium.
It should be pointed out that the critical diameters listed in Table 1 are only theoretical values, and factors of specific instruments should be considered in practical applications. Factors such as settlement height, settlement time and system response time. For specific instruments (such as BT-1500), the actual critical diameter is generally between 2/3 and 1/2 of the value in Table 1. In this way, on the one hand, it is ensured that the measurement is carried out in the laminar flow area; on the other hand, the system has sufficient response time to avoid the leakage of large particles. Influenced by factors such as Brownian motion, the lower limit of the critical diameter of gravity settlement is generally about 3 microns.
3. Centrifugal sedimentation method: For finer particles, the gravity sedimentation method requires a longer sedimentation time, and is greatly affected by convection, diffusion, Brownian motion and other factors during the sedimentation process, resulting in larger measurement errors. In order to overcome these problems, centrifugal sedimentation is usually used to accelerate the sedimentation speed of fine particles, so as to shorten the measurement time and improve the measurement accuracy. In the centrifugal state, the particles are subjected to two opposing forces, one is centrifugal and the other is resistance.
We are professional manufacturer, which is established in 2005 and
focus on export business to Europe, USA and Australia.
We specialized in producing various kinds of Paper napkins, like
dispenser napkin paper. We can produce at 32cm x 32cm, 33cm x 22cm etc.
We can print 1 or 2 color logo on the napkins. The water ink that
we used reach European Food contact grade..
We supply different kinds of materials for Dispenser napkin paper
products, like Virgin, Recycled and Bamboo Pulp (Tree free).
The napkin material is 00% biodegradable and compostable, Chlorine
free and reach food contact grade standard.



Dispenser Paper Napkin,Printed Dispenser Napkin,Personalized Dispenser Napkins,Custom Printed Dispenser Napkins
Bobo Tissue Product Manufacturer , https://www.bobotissues.com